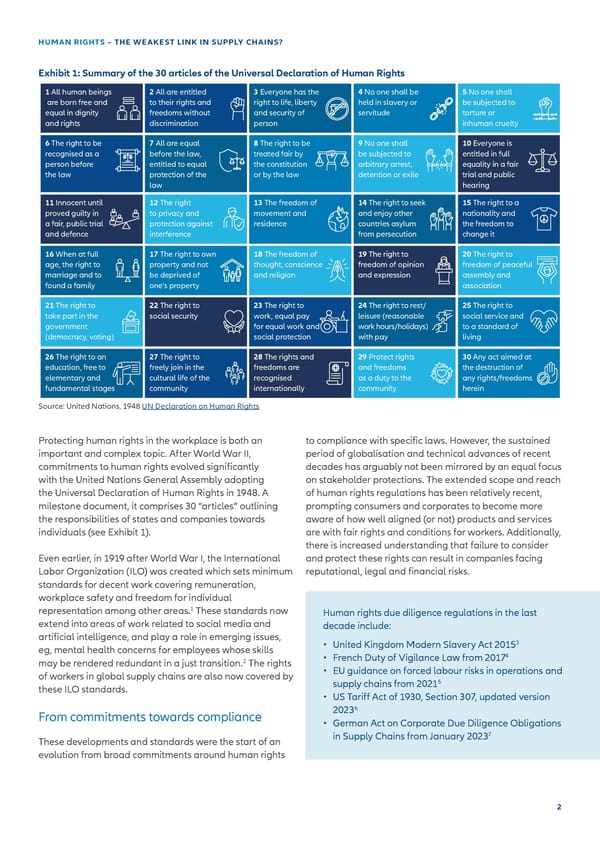
HUMAN RIGHTS – THE WEAKEST LINK IN SUPPLY CHAINS? Exhibit 1: Summary of the 30 articles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1 All human beings 2 All are entitled 3 Everyone has the 4 No one shall be 5 No one shall are born free and to their rights and right to life, liberty held in slavery or be subjected to equal in dignity freedoms without and security of servitude torture or and rights discrimination person inhuman cruelty 6 The right to be 7 All are equal 8 The right to be 9 No one shall 10 Everyone is recognised as a before the law, treated fair by be subjected to entitled in full person before entitled to equal the constitution arbitrary arrest, equality in a fair the law protection of the or by the law detention or exile trial and public law hearing 11 Innocent until 12 The right 13 The freedom of 14 The right to seek 15 The right to a proved guilty in to privacy and movement and and enjoy other nationality and a fair, public trial protection against residence countries asylum the freedom to and defence interference from persecution change it 16 When at full 17 The right to own 18 The freedom of 19 The right to 20 The right to age, the right to property and not thought, conscience freedom of opinion freedom of peaceful marriage and to be deprived of and religion and expression assembly and found a family one’s property association 21 The right to 22 The right to 23 The right to 24 The right to rest/ 25 The right to take part in the social security work, equal pay leisure (reasonable social service and government for equal work and work hours/holidays) to a standard of (democracy, voting) social protection with pay living 26 The right to an 27 The right to 28 The rights and 29 Protect rights 30 Any act aimed at education, free to freely join in the freedoms are and freedoms the destruction of elementary and cultural life of the recognised as a duty to the any rights/freedoms fundamental stages community internationally community herein Source: United Nations, 1948 UN Declaration on Human Rights Protecting human rights in the workplace is both an to compliance with speci昀椀c laws. However, the sustained important and complex topic. After World War II, period of globalisation and technical advances of recent commitments to human rights evolved signi昀椀cantly decades has arguably not been mirrored by an equal focus with the United Nations General Assembly adopting on stakeholder protections. The extended scope and reach the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948. A of human rights regulations has been relatively recent, milestone document, it comprises 30 “articles” outlining prompting consumers and corporates to become more the responsibilities of states and companies towards aware of how well aligned (or not) products and services individuals (see Exhibit 1). are with fair rights and conditions for workers. Additionally, there is increased understanding that failure to consider Even earlier, in 1919 after World War I, the International and protect these rights can result in companies facing Labor Organization (ILO) was created which sets minimum reputational, legal and 昀椀nancial risks. standards for decent work covering remuneration, workplace safety and freedom for individual 1 representation among other areas. These standards now Human rights due diligence regulations in the last extend into areas of work related to social media and decade include: arti昀椀cial intelligence, and play a role in emerging issues, 3 eg, mental health concerns for employees whose skills • United Kingdom Modern Slavery Act 2015 4 may be rendered redundant in a just transition.2 The rights • French Duty of Vigilance Law from 2017 • EU guidance on forced labour risks in operations and of workers in global supply chains are also now covered by 5 these ILO standards. supply chains from 2021 • US Tari昀昀 Act of 1930, Section 307, updated version 6 From commitments towards compliance 2023 • German Act on Corporate Due Diligence Obligations 7 in Supply Chains from January 2023 These developments and standards were the start of an evolution from broad commitments around human rights 2
 Human rights Page 1 Page 3
Human rights Page 1 Page 3