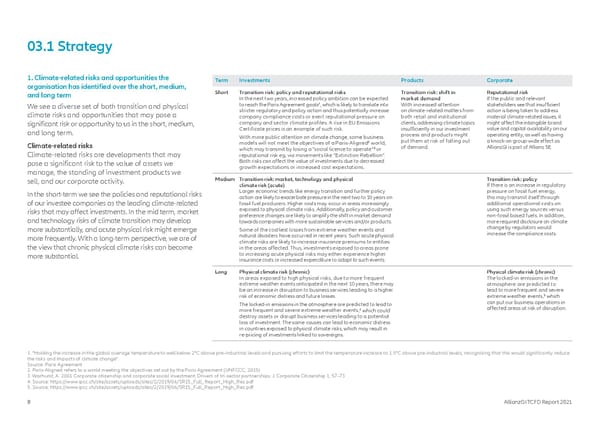
03.1 Strategy 1. Climate-related risks and opportunities the Term Investments Products Corporate organisation has identified over the short, medium, and long term Short Transition risk: policy and reputational risks Transition risk: shift in Reputational risk In the next two years, increased policy ambition can be expected market demand If the public and relevant 1 With increased attention stakeholders see that insufficient We see a diverse set of both transition and physical to reach the Paris Agreement goals , which is likely to translate into climate risks and opportunities that may pose a stricter regulatory and policy action and thus potentially increase on climate-related matters from action is being taken to address company compliance costs or exert reputational pressure on both retail and institutional material climate-related issues, it significant risk or opportunity to us in the short, medium, company and sector climate profiles. A rise in EU Emissions clients, addressing climate topics might affect the intangible brand and long term. Certificate prices is an example of such risk. insufficiently in our investment value and capital availability on our With more public attention on climate change, some business process and products might operating entity, as well as having Climate-related risks models will not meet the objectives of a Paris-Aligned2 world, put them at risk of falling out a knock-on group-wide effect as which may transmit by losing a “social licence to operate”3 or of demand. AllianzGI is part of Allianz SE. Climate-related risks are developments that may reputational risk eg, via movements like “Extinction Rebellion”. pose a significant risk to the value of assets we Both risks can affect the value of investments due to decreased manage, the standing of investment products we growth expectations or increased cost expectations. sell, and our corporate activity. Medium Transition risk: market, technology and physical Transition risk: policy climate risk (acute) If there is an increase in regulatory In the short-term we see the policies and reputational risks Larger economic trends like energy transition and further policy pressure on fossil fuel energy, action are likely to exacerbate pressure in the next two to 10 years on this may transmit itself through of our investee companies as the leading climate-related fossil fuel producers. Higher costs may occur in areas increasingly additional operational costs on risks that may affect investments. In the mid term, market exposed to physical climate risks. Additionally, policy and customer using such energy sources versus and technology risks of climate transition may develop preference changes are likely to amplify the shift in market demand non-fossil based fuels. In addition, towards companies with more sustainable services and/or products. more required disclosure on climate more substantially, and acute physical risk might emerge Some of the costliest losses from extreme weather events and change by regulators would more frequently. With a long-term perspective, we are of natural disasters have occurred in recent years. Such acute physical increase the compliance costs. the view that chronic physical climate risks can become climate risks are likely to increase insurance premiums to entities in the areas affected. Thus, investments exposed to areas prone more substantial. to increasing acute physical risks may either experience higher insurance costs or increased expenditure to adapt to such events. Long Physical climate risk (chronic) Physical climate risk (chronic) In areas exposed to high physical risks, due to more frequent The locked-in emissions in the extreme weather events anticipated in the next 10 years, there may atmosphere are predicted to be an increase in disruption to business services leading to a higher lead to more frequent and severe risk of economic distress and future losses. extreme weather events,5 which The locked-in emissions in the atmosphere are predicted to lead to can put our business operations in more frequent and severe extreme weather events,4 which could affected areas at risk of disruption. destroy assets or disrupt business services leading to a potential loss of investment. The same causes can lead to economic distress in countries exposed to physical climate risks, which may result in re-pricing of investments linked to sovereigns. 1. “Holding the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, recognizing that this would significantly reduce the risks and impacts of climate change”. Source: Paris Agreement 2. Paris-Aligned refers to a world meeting the objectives set out by the Paris Agreement (UNFCCC, 2015) 3. Warhurst, A. 2001 Corporate citizenship and corporate social investment: Drivers of tri-sector partnerships. J. Corporate Citizenship 1, 57–73 4. Source: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2019/06/SR15_Full_Report_High_Res.pdf 5. Source: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2019/06/SR15_Full_Report_High_Res.pdf 8 AllianzGI TCFD Report 2021
 TCFD Report Page 7 Page 9
TCFD Report Page 7 Page 9