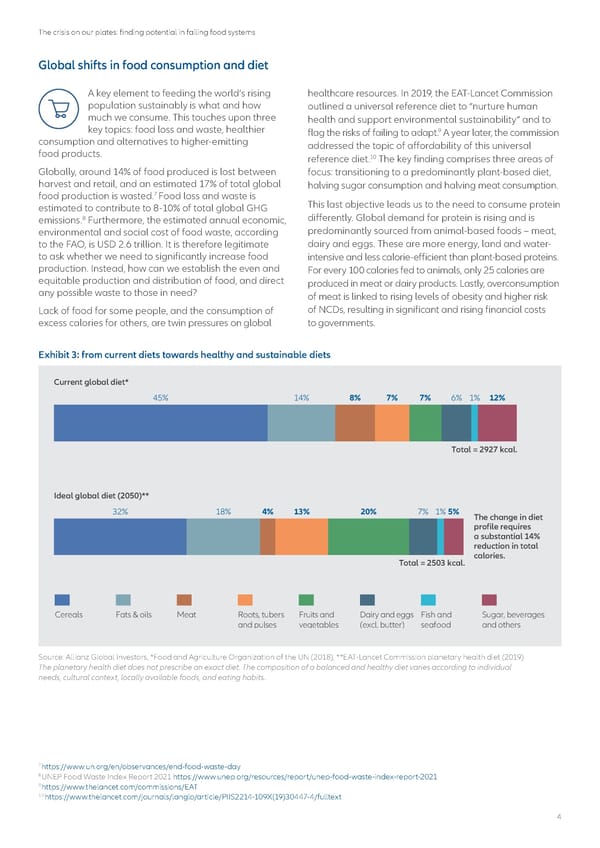
The crisis on our plates: finding potential in failing food systems Global shifts in food consumption and diet A key element to feeding the world’s rising healthcare resources. In 2019, the EAT-Lancet Commission population sustainably is what and how outlined a universal reference diet to “nurture human much we consume. This touches upon three health and support environmental sustainability” and to key topics: food loss and waste, healthier 9 consumption and alternatives to higher-emitting flag the risks of failing to adapt. A year later, the commission food products. addressed the topic of affordability of this universal 10 reference diet. The key finding comprises three areas of Globally, around 14% of food produced is lost between focus: transitioning to a predominantly plant-based diet, harvest and retail, and an estimated 17% of total global halving sugar consumption and halving meat consumption. 7 food production is wasted. Food loss and waste is This last objective leads us to the need to consume protein estimated to contribute to 8-10% of total global GHG emissions.8 Furthermore, the estimated annual economic, differently. Global demand for protein is rising and is environmental and social cost of food waste, according predominantly sourced from animal-based foods – meat, to the FAO, is USD 2.6 trillion. It is therefore legitimate dairy and eggs. These are more energy, land and water- to ask whether we need to significantly increase food intensive and less calorie-efficient than plant-based proteins. production. Instead, how can we establish the even and For every 100 calories fed to animals, only 25 calories are equitable production and distribution of food, and direct produced in meat or dairy products. Lastly, overconsumption any possible waste to those in need? of meat is linked to rising levels of obesity and higher risk Lack of food for some people, and the consumption of of NCDs, resulting in significant and rising financial costs excess calories for others, are twin pressures on global to governments. Exhibit 3: from current diets towards healthy and sustainable diets Current global diet* 45% 14% 8% 7% 7% 6% 1% 12% Total = 2927 kcal. Ideal global diet (2050)** 32% 18% 4% 13% 20% 7% 1%5% The change in diet profile requires a substantial 14% reduction in total Total = 2503 kcal. calories. Cereals Fats & oils Meat Roots, tubers Fruits and Dairy and eggs Fish and Sugar, beverages and pulses vegetables (excl. butter) seafood and others Source: Allianz Global Investors, *Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (2018), **EAT-Lancet Commission planetary health diet (2019) The planetary health diet does not prescribe an exact diet. The composition of a balanced and healthy diet varies according to individual needs, cultural context, locally available foods, and eating habits. 7https://www.un.org/en/observances/end-food-waste-day 8UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2021 https://www.unep.org/resources/report/unep-food-waste-index-report-2021 9https://www.thelancet.com/commissions/EAT 10https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(19)30447-4/fulltext 4
 The crisis on our plates: finding potential in failing food systems Page 3 Page 5
The crisis on our plates: finding potential in failing food systems Page 3 Page 5